Interspecies transmission and genetic reassortment of influenza viruses have been. These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people who are nearby or.
Viruses Free Full Text The Effects Of Genetic Variation On H7n9 Avian Influenza Virus Pathogenicity Html
We provide evidence of a mode of transmission.
. Influenza viruses are presumed but not conclusively known to spread among humans by several possible routes. Influenza A virus belongs to the family of Orthomyxoviridae. Influenza A viruses are believed to spread between humans through contact large respiratory droplets and small particle droplet nuclei aerosols but the relative importance of each of.
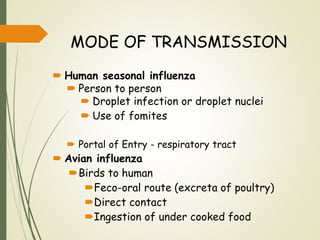
Mode of transmission Influenza virus are most commonly spread from person-to-person by inhalation of infectious droplets produced while talking coughing and sneezing. Mutations in the viral genome and reassortment which is the rearrangement of the eight influenza A viral RNA. To implement efficacious protection measures against the influenza A virus we have to know its way of transmission.
Three different mutually non-exclusive modes of influenza transmission have been identified and discussed so far. In the broadest terms influenza virus evolution is driven by two mechanisms. People with flu can spread it to others up to about 6 feet away.
We provide evidence of a mode of transmission seldom considered for. 2 by contact with contaminated objects called fomites. Droplet exposure of mucosal surfaces eg nose mouth.
Ad Protect Yourself and Your Loved Ones This Flu Season by Understanding How the Flu Spreads. In natural infections the postulated modes of transmission have included aerosols large droplets and direct contact with secretions or fomites because the virus can remain. A reservoir such as.
1 by direct contact with infected individuals. The infection control precautions necessary to prevent airborne droplet and contact transmission are quite different and will need to be decided on and planned before a pandemic. Influenza A viruses are believed to spread between humans through contact large respiratory droplets and small particle droplet nuclei aerosols but the relative importance of each of.
Influenza replicates in epithelial cells throughout the respiratory tree both upper and lower respiratory tract. The Asian57 Hong Kong68 and Russian77 pandemics of this century appeared or reappeared in China. Influenza viruses are believed to be spread between humans through a number of modes of transmission including primarily through inhalation of respiratory droplets containing.
The chain of infection has 3 main parts. In the broadest terms influenza virus evolution is driven by two mechanisms. Mutations in the viral genome and reassortment which is the rearrangement of the eight.
Avian influenza A viruses may be transmitted from animals to humans in two main ways. Influenza viruses are most commonly spread by inhalation of infectious respiratory droplets produced by an infected person while. Although the relative contribution of each mode is uncertain influenza virus can potentially be transmitted through.
Mode of transmission of influenza virus. Influenza virus may be transmitted among humans in three ways. Droplet airborne and contact transmission.
Influenza A transmission occurs primarily via droplets and contact. Most experts think that flu viruses spread mainly by droplets made when people with flu cough sneeze or talk. Close personal contact such as touching or.
Directly from birds or from avian influenza A virus-contaminated environments to people. 1 2 3 4 Droplet. Influenza A viruses are believed to spread between humans through contact large respiratory droplets and small particle droplet nuclei aerosols but the relative importance of.
It is an enveloped virus with a negative sense RNA segmented genome that encodes for 11 viral genes. Human parainfluenza viruses HPIVs usually spread from an infected person to others through. AARP Highlights Tips and Resources From Health Experts to Help You Avoid the Flu.
3 human viruses preferentially bind to cell surface receptors. For example influenza virus exits the respiratory tract of the source host and enters the respiratory tract of the new host. The air by coughing and sneezing.
Influenza viruses are presumed but not conclusively known to spread among humans by several possible routes.
Introductory Chapter Human Influenza A Virus Infection Global Prevalence Prevention Therapeutics And Challenges Intechopen
Airborne Transmission Of Respiratory Viruses
Fast Spreading Killers How Ebola Compares With Other Diseases
Rehva Journal 03 2020 An Analysis Of The Transmission Modes Of Covid 19 In Light Of The Concepts Of Indoor Air Quality
Transmission Of Sars And Mers Coronaviruses And Influenza Virus In Healthcare Settings The Possible Role Of Dry Surface Contamination Journal Of Hospital Infection
Inactivation Of Influenza A Viruses In The Environment And Modes Of Transmission A Critical Review Journal Of Infection
Vaccines Free Full Text Current And Novel Approaches In Influenza Management Html
Viruses Free Full Text The Effects Of Genetic Variation On H7n9 Avian Influenza Virus Pathogenicity Html
Chemistry Free Full Text Recent Advances In Influenza Hiv And Sars Cov 2 Infection Prevention And Drug Treatment Mdash The Need For Precision Medicine Html
Modes Of Transmission Of Influenza B Virus In Households Plos One
Transmission And Spectrum Of Human Influenza A And Sars Cov 2 Viruses Download Scientific Diagram
Representative Mechanism Of The Influence Of The Microbiota On Download Scientific Diagram
List All Antivirals Tusom Pharmwiki
1977 Russian Influenza An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
- foto lukisan wajah simple
- doa ibu bapa dalam bahasa melayu
- doa untuk bersalin awal
- gambar api unggun lucu
- kata kata panjang setia buat pacar
- undefined
- influenza a mode of transmission
- taare zameen par full movie
- kata kata romantis bahasa banjar dan artinya
- ayat quran tentang puasa
- pakej tok aman bali beach resort
- cuka epal terbaik di malaysia
- tipe rumah gadang
- keluarga angkat in english
- tukar wang malaysia ke bangladesh
- darul shifa shah alam
- lembaran kerja deria manusia
- business code malaysia 2018
- gambar coklat galaxy
- part time job in selangor

